AWPs helping work at heights efficiently, safely, quickly and easily
By Edit Team | February 19, 2014 8:31 am SHARE
Aerial work platforms provide a much safe alternative for working at heights when compared with traditional scaffoldings
Though aerial work platform (AWP) is common equipment on any job site in the developed countries, its usage in India has just started few years ago. However, the general awareness of aerial work platforms is on the rise and we are sure to see a huge rise is the usage of work platforms. AWPs are also known as elevating work platforms (EWP), mobile elevating work platforms (MEWP), man lifts, boom lifts and cherry picker.
Essentially, these equipment are used to provide temporary access for people to difficult to reach areas at heights. They are generally used to provide temporary, quick, flexible and safe access for maintenance and construction work. These machines are designed to lift limited weight, usually less than a tonne thus distinguishing them from most types of cranes. Many times, people confuse aerial platforms with cranes. Cranes are designed primary to lifts loads whereas the aerial platforms are for lifting people. In simple words, AWP lift workers, tools and supplies for the completion of different types of work at height.
Aerial work platforms certainly provide a much safe alternative for working at heights when compared with traditional scaffoldings. No matter where you need access at heights, the AWP can provide you the solution. There are different types of platforms to cater to different needs. Compact AWP fit through standard doorways and can be used indoors too. Rough Terrain AWP allows one to work in areas that do not offer smooth floor (mostly in green field projects). AWPs offer huge productivity gains over ladders and scaffolds. Ladders do not provide the reach and mobility that AWPs provide, and the scaffolds take a long time to put up and relocate to a new area. The worker fatigue is also considerably reduced with AWPs which in turn increases productivity. AWPs also provide flexibility in a variety of areas like HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning), electrical installations, plumbing and sprinkler systems, regular maintenance, cleaning, painting and decorations.
AWPs come in a variety of types — right from a push around personnel lifts for working at a height of 10 feet up to a truck mounted boom lift that can reach as high as 300 feet. There are different types of AWPs designed for different applications. Following are the broad classifications of AWPs:
• Personnel lifts (mast lifts): In this type, the work platform is supported by a slender vertical or near vertical structure. In some designs, it can also provide a limited horizontal outreach but mostly these are vertical lifts. In some cases, there are dual masts which allow the platform to be taken to more heights. Normally 45 feet is the maximum heights that can be achieved with these.
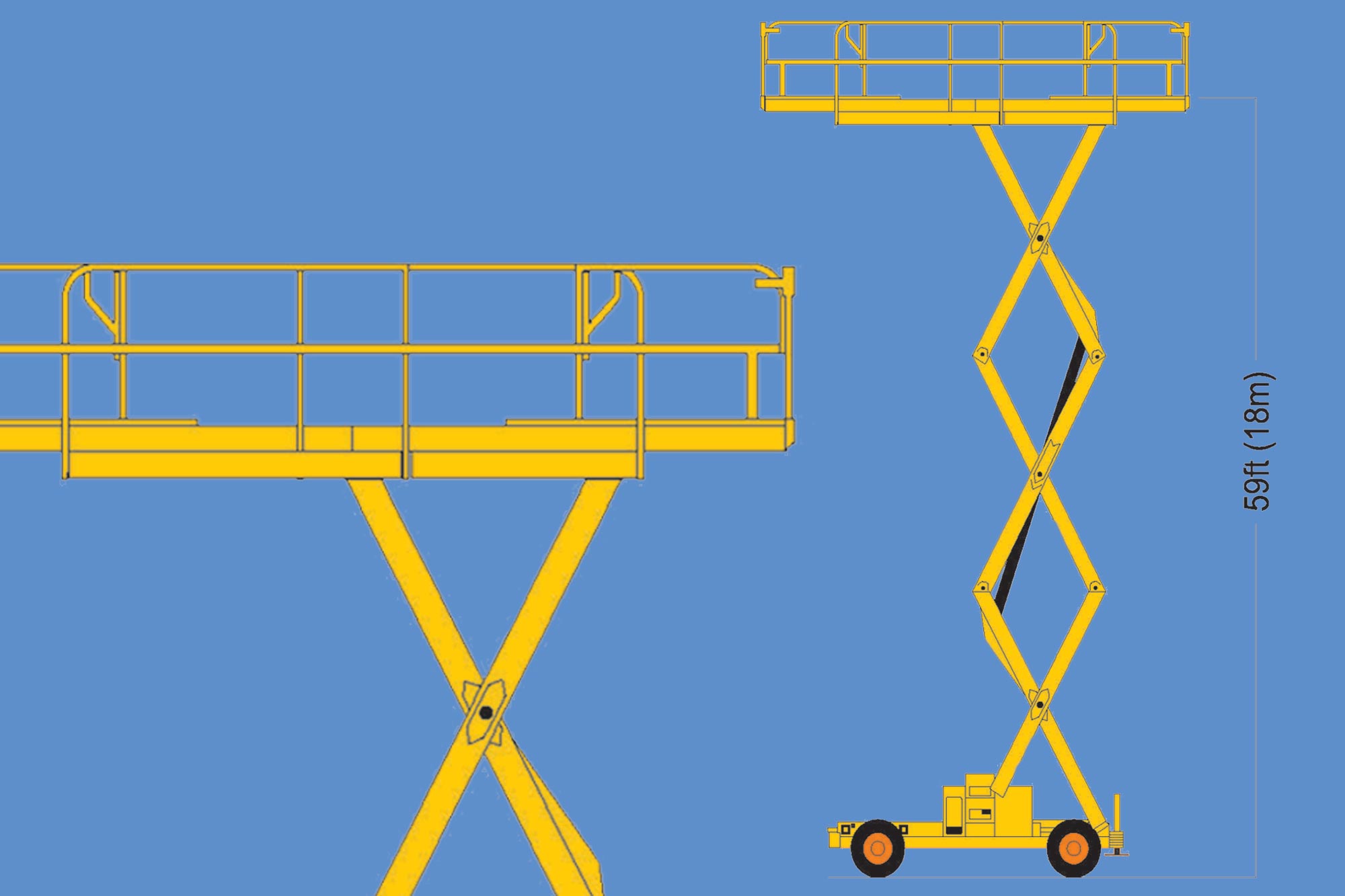
• Scissor lifts: The name comes because of its resemblance to an oversized scissor with criss-cross support. The work platform is lifted vertically above the equipment’s wheel base. Hence these AWP work well for applications requiring access directly overhead. Few types of scissor lifts also provide a large platform size with capacities in excess of a tonne with working height as high as 60 feet. Such large machines operate on outrigger support when needed to work at that height. Scissor lifts are available both in electric driven as well as diesel driven.
• Telescopic boom lifts: As the same suggests, in these type the work platform is mounted on a straight boom that can be extended to the desired working heights. These AWPs have the ability of raise the boom to a vertical position as well as lower to a below horizontal position. These types come in working heights, ranging from 30 feet up to 135 feet. When compared to the articulated type of AWPs, these types are simpler and easier to operate and provide a longer horizontal outreach. These also
come in electric-driven and diesel-driven models.
• Articulating boom lifts: These types of boom lifts are used whenever we need to go up and above some immovable obstacles, in addition to going up. Available platform heights commonly range from 30 to 60 feet on electric models and from 30 to 150 feet on diesel driven machines. Horizontal outreach may vary from 10 feet up to 30 feet.
With so many options to choose from, selecting the right type of aerial work platform might be confusing. Many factors determine the selection such as whether you are working inside or outside, availability of electricity, type of terrain you will work on, the height to be reached, whether you need to reach up, and the load bearing capacity of the ground on which you will be working. Broadly you need to look at the following features for deciding the right type of AWP for your job:
• Power source: Areas like running factories might not permit exhaust fumes coming out of a diesel powered AWP. In such cases, electrically operated machine has to be used. Mostly the electrically operated machines are designed to be used indoors. But there are some models that can be used outdoors too. There are few types that are dual energy, i.e. diesel and electrically operated. New construction sites that have a rough terrain and no power mostly require diesel-driven machines.
• Maximum reach: This parameter must be carefully worked at. Most of the manufacturers specify the working height in the catalogues and not the platform height. The platform height is the maximum height to which you can raise the platform while the working height indicates the level that an average worker can reach while at the maximum platform height. Normally, the maximum working height is 6 feet more than the maximum platform height. The horizontal outreach is also an important parameter for proper selection of an AWP. The stowed dimensions will also play an important role in certain cases, where the AWP has to travel under some restrictions like pipe racks etc. The tail swing can also be important where the AWP is working in confined spaces. Tail swing is the dimension by which the revolving super structure of the AWP protrudes out of the chassis.
• Gradability: This parameter is normally expressed in percentage. This defines the maximum slope the AWP can climb while travelling. Some AWP can work only on flat surfaces while some rough terrain machines can tackle sites with slopes as high as 50 per cent.
• Platform size: AWPs come with various sizes of platforms. The platform size should allow the workers on it to work comfortably. Scissor lifts normally have largest platform sizes and are also equipped with extension decks to allow you to expand the size of the platform size. Normally, there are two anchor points where the workers can anchor their safety belts.
• Weight: AWPs can easily weigh anywhere from 200 kg for a small, manual AWP to as much as 20,000 kgs for a big telescopic AWP. You will have to check the weight of the AWP to make sure that the surface you will use it on can support it.
• Load capacity: While most of the smaller AWPs have only capacity over the entire working range, the larger AWPs tend to provide two capacities — restricted and unrestricted. This means in some working area, the AWP has higher capacities and a lower capacity over the entire range. This rating usually is depicted on the working range chart of the equipment and known as working envelope chart. Such large AWPs usually have a load limiter to ensure that the AWP is not operated beyond its specified capacity.
• Safety features: In addition to the overload protection devices, there are few other important safety features that may decide their selection based on your application area. Some of them are platform levelling, tilt alarm, descent alarm, lanyard attachment points, pothole prevention system, oscillating axles etc.
• Optional features: Most of the manufacturers provide a lot of optional features so as to make the AWP more versatile. Non-marking tires, auto levelling out riggers, on board power generators for power tools, welder package, compressed air provision, pipe handling attachment and glass sheet handler are a few optional features that can play a decisive role in the selection of AWP.
AWPs certainly help one complete the work at heights efficiently, safely, quickly and easily. AWPs also come with their set of risks and disadvantages. Injuries, sometimes fatal, can result from accidents, tip over, collapse, collision and falling off the basket. For these reasons, this becomes mandatory that only a trained person operates the AWP. It requires a certain minimum skill set to keep the AWPs in good condition. The rising number of AWPs will need a large number of technically expert service personnel in the coming years.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.