Decoding industrial paint coatings: From green technology to skill development
By Staff Report | January 15, 2025 6:44 pm SHARE

The following article provides brief information on paint coatings to summarise some of the important queries people have on issues like paint selection, application, different types of paint systems, sustainability, green technology, eco-friendliness, nanotechnology, and the importance of training and skill development in paint coatings.
Indian Paint Market is now reaching 75,000 CR, soon crossing a target of one lakh crore by 2028. This cost includes the cost of manufacturing paints, raw materials, dealership and distribution, paint application by contractors, R & D and paint training and consultancy programs. Naturally, people ask where we stand today and what the upcoming and new technologies are. Is sustainability considered the main factor, and is eco-friendly and using green products another requirement? Let us take these issues one by one:
A conventional paint system combines resin, solvent, pigment and additives. The consumption of the paint depends upon the volume of the paint: a higher volume solid paint gives higher thickness and hence is consumed less, while paint with a lower volume solid gives lower thickness per coat and releases more VOC ( volatile content – solvent), which is responsible for creating pollution. Therefore, paint made without solvents is called Solventless coatings, and those made in alternate solvents such as water are called Green and eco-friendly paints. Solventless coatings also come under the High-Performance category as these coatings have durability in the range of 5 to 15 years and can be applied in very toxic environments.
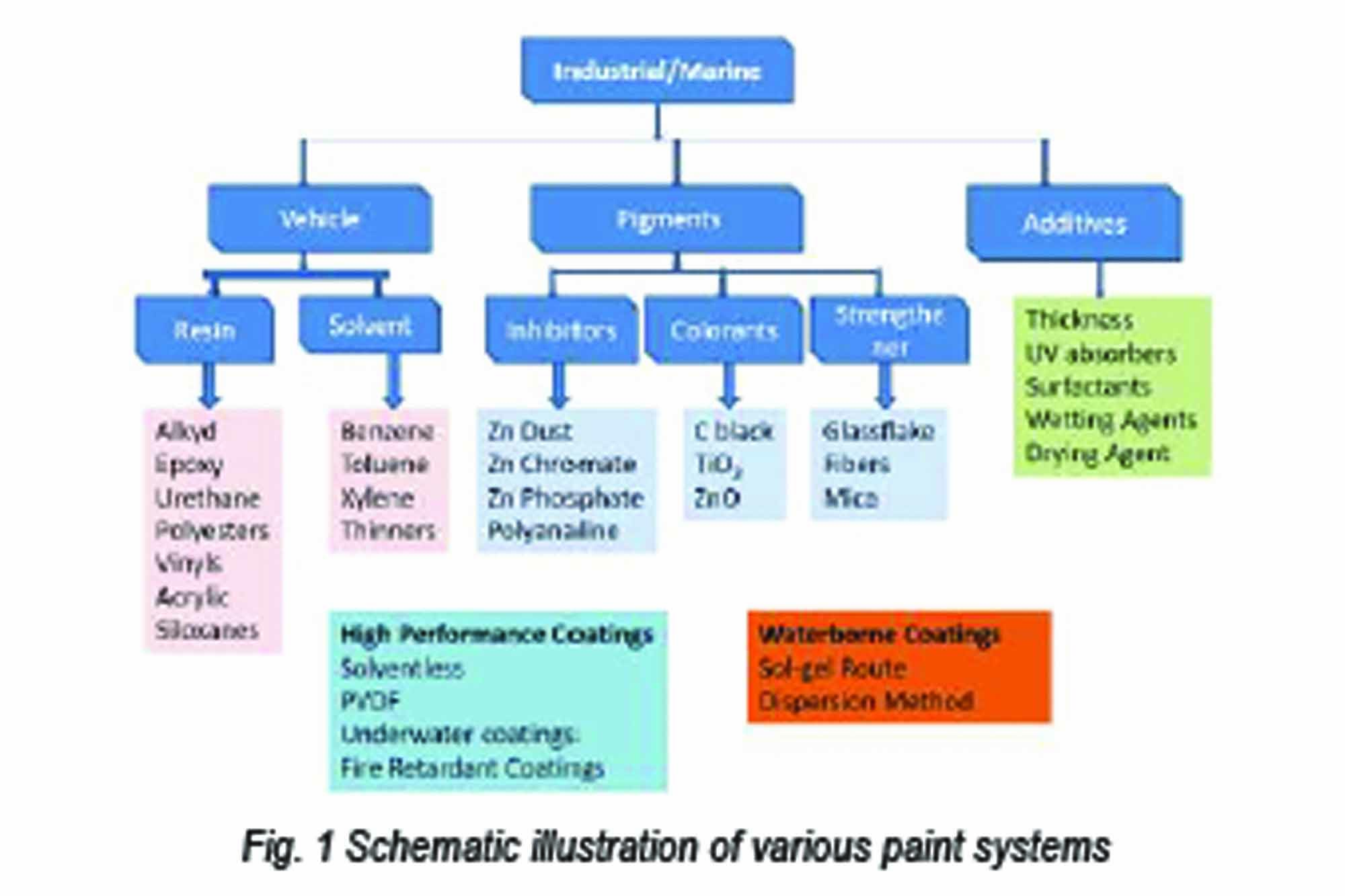
Solventless coatings are a big requirement for many Industrial applications, where paints of higher thickness ranging from 500 to 2000 microns are required. They are eco-friendly and can be applied very quickly using an airless gun. Waterborne coating is another example of eco-friendly coating; this technology is progressing well. In the case of buildings and concrete structures, almost 70-75 percent of paints used are waterborne, but for steel base structures, waterborne technology is still far behind. Not only are waterborne coatings costly, but they are unable to provide the same durability as solvent-based coatings.
Another improvement in the coating industry is the use of Functional Coatings. These coatings solve the specific problem of a structure or substrate. Coatings are applied to take care of several functions of a substrate: corrosion resistance, erosion, water repellence, dust removal, imparting conductivity to the surface, and many more. Functional coatings serve to provide one or more functions to the substrate.
The next category of coatings is Smart coatings. A smart coating is one that provides some action on the surface, very similar to tackling one of the coating’s functions. Examples: Self-cleaning coatings—when applied, they are responsible for cleaning the substrate using a drop of water coming from dew, which is moisture deposition. Another example is self-healing coatings, which help prolong the life of the coating by healing a damaged coating and thus causing self-repair and prolonging the life of the coating. Nanotechnology has revolutionised the coating industry. This single technology has helped in making several Functional and Smart coatings
What is nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology in paint means either the use of nanosized polymer resin or the use of nanosized pigments or additives. Nanosized pigment/additives, if used, give the following advantages: reduced quantity of raw materials, higher corrosion resistance with long durability mainly due to even distribution of particles with large surface area, higher tensile strength and thus resistance to rupture and special properties such as water repellence anti-microbial properties etc.

The final issue is sustainability. It is an issue in paint coating, which is very widely discussed in paint coating discussions but hardly implemented. Sustainability basically means reuse of the material, recyclability, making by a lower energy process, green product, and perhaps a few more. In paint coatings, there has been a good awareness of the use of green, eco-friendly paints, as discussed above, as well as solventless and waterborne coatings. There is the use of many natural products from which several raw materials, including resins, are made. Recycling is still a problem when high-class plastic polymer films are used. Usually, paint films burn at temperatures above 300-400oC but leave a lot of carbon in the atmosphere.
One thing that can improve the paint industry is systematic training, counselling, and skill development. Paint coating is art as well as Science. Selection of coating is extremely important. There are thousands of formulations, and unless the user has the basic knowledge to select a suitable paint for his application, he will never get the satisfaction and life he is expecting. The application of paint is art. Today, there are very simple methods, from Dip Coating to application by brush and roller to instrumental methods such as air spray and airless spray; each needs special training to get the best application that looks aesthetically and also provides good durability. There are several training schools and groups, but people do not attend and try to think that applying for paint is a trivial process. This is the mistake they make, and it ultimately ends in poor application and performance.
For more information, visit: https://www.sspcindia.org/
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.




































-20240213125207.png)

























