Saving cost by strengthening and widening existing roads
By Edit Team | July 2, 2015 12:31 pm SHARE
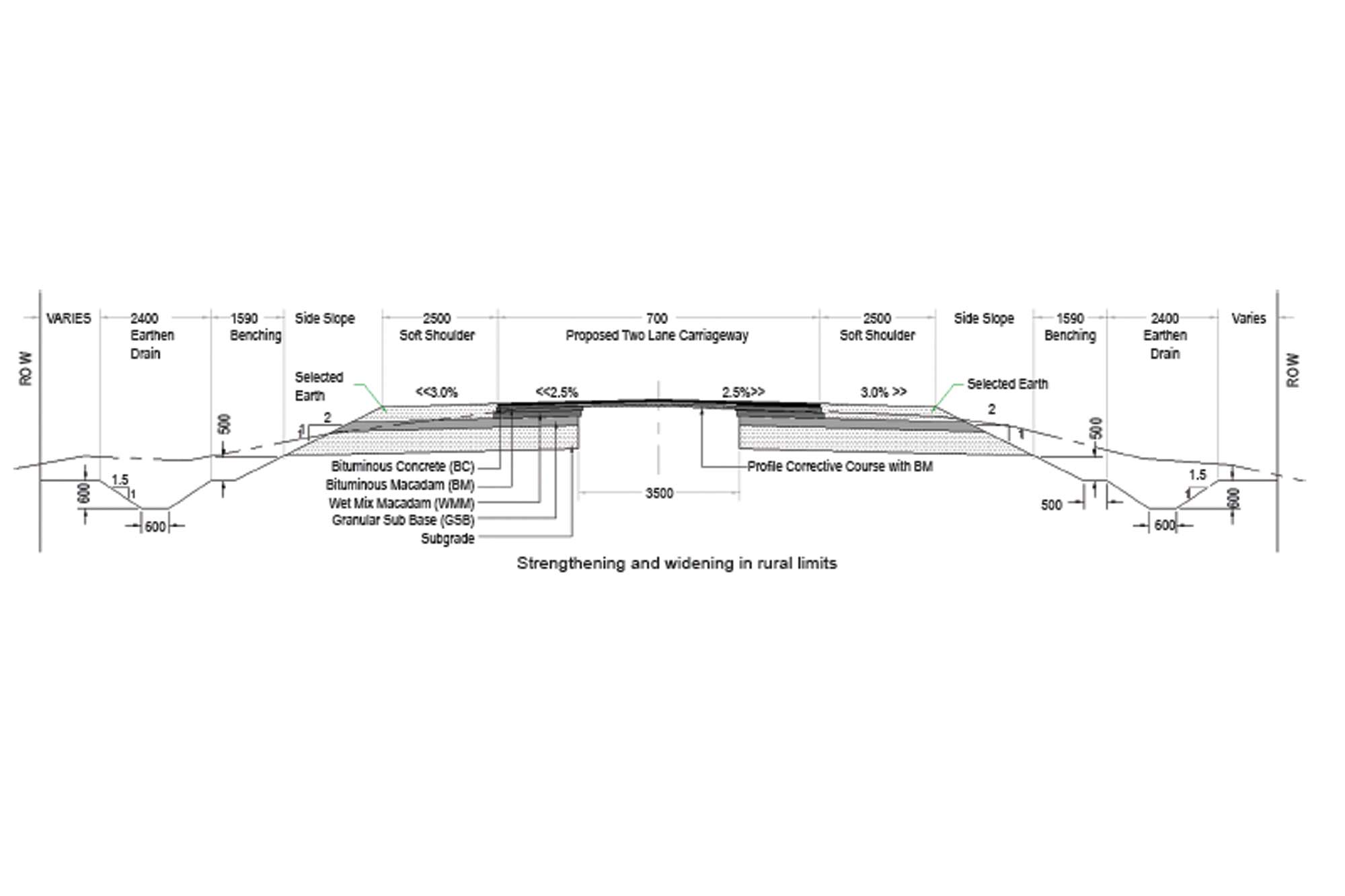
When a project is proposed for strengthening and widening, the geometric and pavement design plays a very important role to blend
The Indian government is getting ready to unveil an ambitious project aimed at making a vast improvement to the country’s roads — upgrading existing ones and building new links to connect remote areas in the hinterland. Cabinet notes have been prepared for the various programs like Sethu Bharatam (150 railway over bridges and 204 level crossings), Rashtriya Rajmarg Zila Sanjoyukta Pariyojana (Over 5,600 kms of highways linking 123 district headquarters to NH network), Bharatmala (5,500 kms stretch connecting border states), roads to hinterland (2,000 kms project linking in underdeveloped areas in non-naxal belts to the NH networks, and religious circuit by developing a 2,000-km stretch connecting Nanded and Katra.
The existing roads in good condition which are proposed to be retained partially or fully with respect to the crust layers and also widening is taken up are termed as strengthening and widening projects. This type of construction has many advantages, mainly it’s economical and it speeds up the construction. It also facilitates to retain the compaction of the layers which has been hardened over a period of years. The main disadvantage is that the land acquisition may be required on one side and the project may have to face the wrath of the localities.
When a project is proposed for strengthening and widening, the geometric and pavement design plays a very important role to blend the alignment and crust to the existing road without compromising the requirements and specifications as required by the proposed road corridor. The design engineer will carefully study the existing road geometrics, location of structures, built-up areas etc, so that the proposed center line of the project will be designed in such way that it utilizes the maximum resources of the existing road. In most of the cases a small thickness layer of structural layer like DBM/BM/BC is used to provide the correction to the existing surface and is called as a profile corrective course. As the name indicates it is a layer which is constructed for only the correction of the profile of the existing road black topped surface. The above layers of the road are constructed as a full depth design layers. The drawings below depict the procedure.
As it is clearly understood that strengthening and widening projects will be a vital projects which will be taken up for the infrastructure development, ESurveying Softech, has developed a comprehensive package called “ESurvey CADD” to address the strengthening and widening projects in more efficient, accurate and with minimum time .The software not only addresses this type of roads, but also is capable of developing road corridors on virgin alignments with reconstruction.
The drawings below depict the concept.
Ayanakanti Murali babu is the road design, domain expert at ESurveying and has automated many processes related to road designing by using his rich exposure of designing national highway, rail and road projects. With vast experience in preparing detailed project/feasibility reports pertaining to various types of roads projects Mr Babu, has also been involved in several projects in the capacity of Project
Manager, Highway Engineer, Chief Surveyor.
Contact:
Ayanakanti Murali babu
Mobile: +91-9738557731
Email: murali@esurveying.net
www.esurveying.net
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.





































































