Challenges and Rehabilitation of MG SETU Bridge (Patna), BIHAR
By Edit Team | February 15, 2022 4:49 pm SHARE
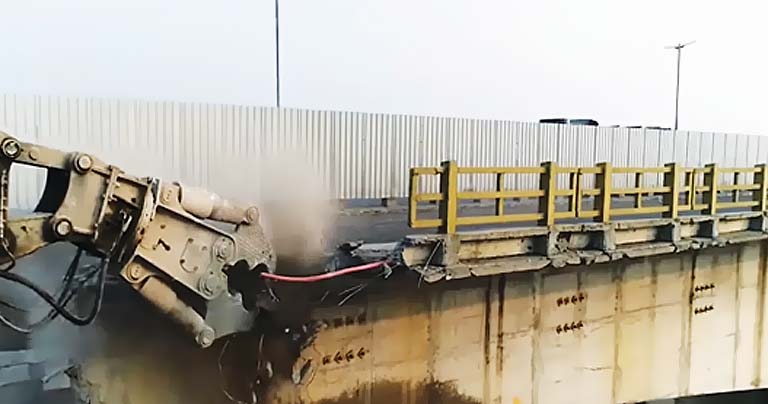

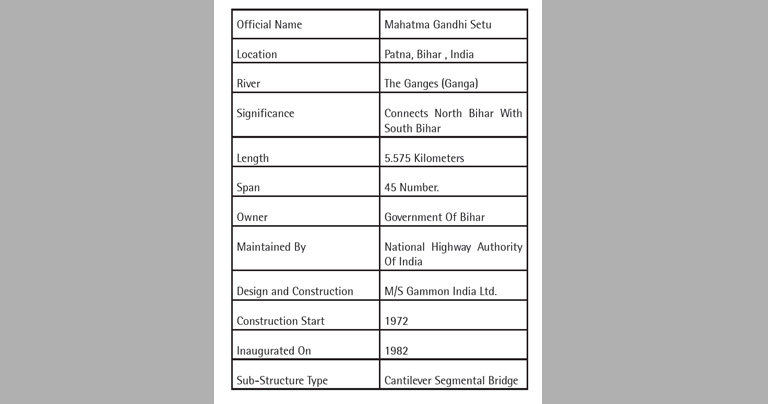
Introduction: Construction by Gammon
The bridge consists of 45 intermediate spans of 121.065 metres (397.19 ft.) each and a span of 65.530 metres (214.99 ft.) at each end. The deck provides 7.5 m (25 ft.) wide two-lane roadways for IRC class 70 R loading with footpaths on either side. The cantilever segmental construction method was adopted to construct this mega bridge.
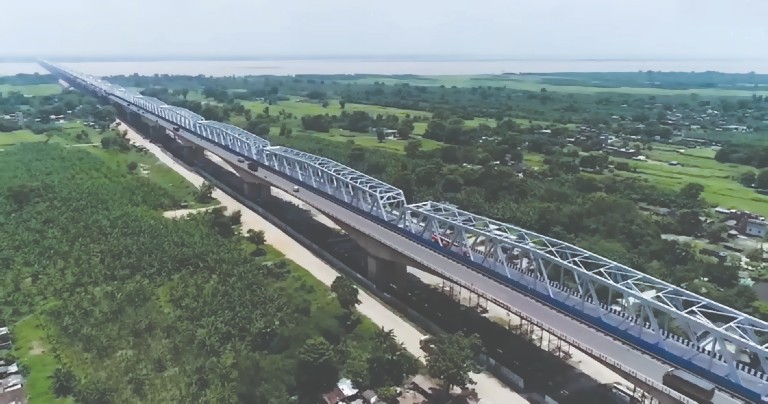
 MG SETU Rehabilitation
MG SETU Rehabilitation
The importance of MG Setu is very critical, as it carries more than 40.000 vehicles per day and provides livelihood to more than 2 lakh people, connecting Bihar to all local markets. Understanding the importance, tenders were floated by MORTH to replace the entire cantilever segment structure with steel truss girders
The project was awarded to M/S AFCONS SIBMOST JV at a cost of 1742 Crores under the PMC of M/S TPF Engineering.
Challenges in this process
The bridge has 46 piers in total, out of which 26 come in the ground zone, 10 numbers in the season flow zone and 10 numbers over the river Ganges. The challenge was that no debris could fall into the holy river. Water spans are in highly current flow zones.
Rehabilitative process
DEXTRA India’s Participation
RepairGrip Couplers
- Dextra India supplied RepairGrip Couplers for the connection of existing bars with new extension bars for the pier cap.
- RG Couplers are 16mm, 20mm, 25mm, 32mm, and Transition Couplers of RG TC32-28 and RG TC25-20.
- Each pier has an average of 280 bars.
A fully threaded bar system
Dextra India supplied a fully threaded bar system to control vibrations of piers while traffic was actively passing through downstream.
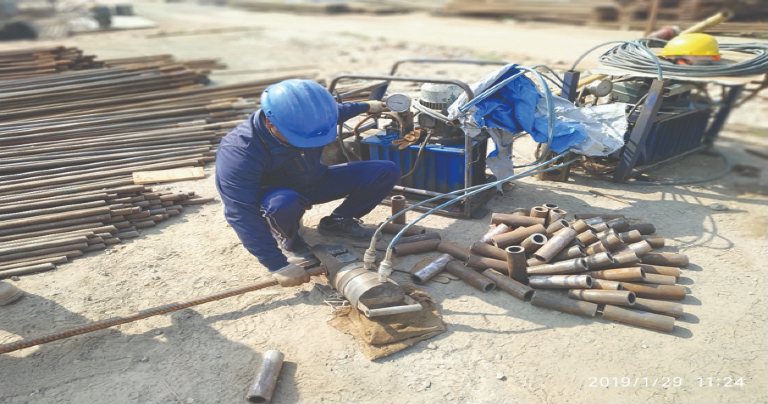 Preparation of single-side crimping at steelyard
Preparation of single-side crimping at steelyard
During the preparation of single-side crimping at steelyard, the Rebar ends are cleaned with the help of a wire brush to clear the rust. The Couplers and Rebars are then marked to ensure that the second bar contain sufficient embedment in sleeve, and finally the sleeves are the punched over Rebar with the help of a hydraulic powerpack.
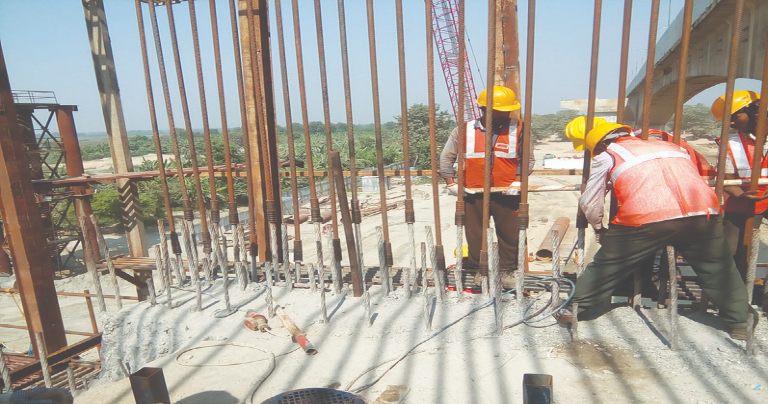
Final crimping at site
Rebar ends are cleaned with the help of a wire brush to clear the concrete and dusts. Existing Rebars are checked and marked by engineer for cutting the heads for proper butt joint.
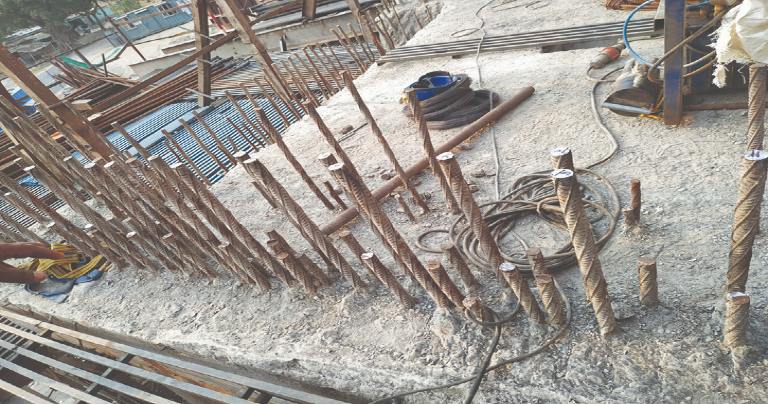 Rebars are then straightened by the help of mechanical tools, after this single side crimped Rebars are placed over the existing bars.
Rebars are then straightened by the help of mechanical tools, after this single side crimped Rebars are placed over the existing bars.
Fully threaded bars at site


(Expertise shared by: Manoj Nayak Application Engineer Dextra India )
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.




































-20240213125207.png)

























